Press Release 19/11/2025
HOSPITAL MORBIDITY STATISTICS. 2024
Admissions to acute care hospitals in the Basque Country increased by 2.7% in 2024
In public hospitals, admissions were up 3.7%, while in private hospitals, they were down 2.1%
In 2024, there were 241,936 admissions to acute care hospitals in the Basque Country, an increase of 2.7% in respect of the previous year, according to Eustat data.
The main causes of hospitalisation were digestive, circulatory and respiratory diseases, which together accounted for 38.5% of admissions (+5.1% compared to 2023).
October was the month with the highest number of hospital admissions (9.3%), while January saw the greatest number of deaths in hospitals (10.5% of the total). Respiratory diseases were also more prevalent in January due to cases of flu and pneumonia.
Nearly 85% of admissions were treated in public hospitals
84.6% of people were treated in public hospitals and 15.4% in private ones. In the latter, the order of frequency of the pathologies treated changed: musculoskeletal problems were the most treated (20.2%), especially osteoarthritis of the hip and knee, and in second place were trauma and injuries (14.1%), with cruciate ligament knee sprains being among the most frequently diagnosed.
63.9% of admissions were emergencies, a percentage that rose to almost 70% in public hospitals (31.4% in private ones). Of the total number of discharges, 90.8% were due to recovery or improvement, 3.4% were due to death, and the rest were due to transfers to other centres or other reasons.
51.3% of hospitalisations corresponded to men
As for the profile of people admitted, the proportion of men (51.3%) was greater than that of women (48.7%), rising to 54.5% if we exclude cases of pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum care. Compared to 2023, hospital admissions were up 3% for men and 2.5% for women.
The 65-79 age group recorded the highest number of hospitalisations
52.3% of people admitted to hospital were over 64 years old, with the 65-79 age group accounting for the highest number of admissions (29.5%), followed by the 45-64 age group (25.3%).
By gender, the 65-79 age range accounted for the majority of hospitalisations among men (nearly 34%), while among women, this majority was distributed almost equally between the 65-79 age group (25%) and those aged 80 and over (24.9%). In fact, women surpassed men in the 80 and over age range.
By province, 51.3% resided in Bizkaia, 31% in Gipuzkoa, 15.1% in Álava, 1.9% in neighbouring provinces (primarily Burgos and Cantabria), 0.4% in other provinces and 0.3% abroad.
Of particular note was the rise in admissions due to diseases of the respiratory system
Among the major groups of illnesses, diseases of the digestive system were the main cause of hospitalisation in 2024 (with 13.4%), closely followed by diseases of the circulatory and respiratory systems (with 12.6% and 12.5%, respectively) and, further behind, by trauma and injuries (9.6%) and tumours (9.3%).
Particularly noteworthy was the increase in the number of admissions due to diseases of the respiratory system, which rose for the third consecutive year (+7.2% compared to 2023). This increase significantly reduced the gap between the two main causes of hospitalisation, placing it on a par with diseases of the circulatory system.
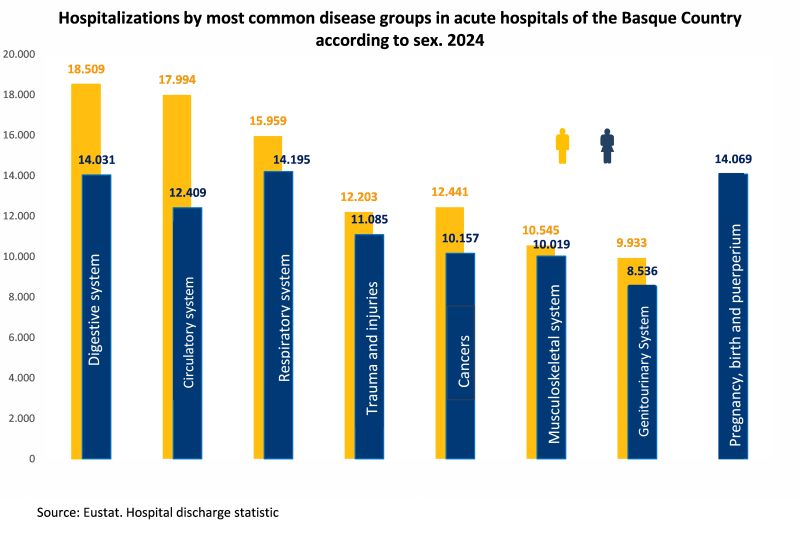
Among men, the order of the three most common causes remained the same: diseases of the digestive system (14.9%), circulatory system (14.5%) and respiratory system (12.9%). For these disease groups, hospital admissions were higher among men than women.
Among women, the continued decline over the last fifteen years (since 2009) in admissions for obstetric procedures has resulted in other common illness groups becoming more prominent, as is the case for respiratory (12%) and digestive diseases (11.9%), which are now practically on a par with pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum care (11.9%).
Hospitalizations by most common disease groups in acute care hospitals in the Basque Country according to sex and age groups. 2024


| |
Total |
% (*) |
Rate of change (%) 2024/2023 |
Sex (%) |
Age (%) |
| |
|
|
|
Man |
Woman |
0-14 |
15-44 |
45-64 |
65-79 |
80 and more |
| LARGE DIAGNOSTIC GROUPS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total |
241,936 |
100 |
2.7 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
| Digestive system |
32,540 |
13.4 |
2.9 |
14.9 |
11.9 |
8.2 |
11.2 |
16.6 |
14.0 |
12.0 |
| Circulatory system |
30,403 |
12.6 |
5.3 |
14.5 |
10.5 |
0.9 |
2.3 |
10.7 |
15.8 |
20.7 |
| Respiratory system |
30,154 |
12.5 |
7.2 |
12.9 |
12.0 |
22.2 |
8.4 |
9.2 |
11.7 |
18.5 |
| Trauma and injuries |
23,288 |
9.6 |
2.8 |
9.8 |
9.4 |
7.8 |
10.8 |
10.8 |
8.0 |
9.9 |
| Tumors |
22,598 |
9.3 |
3.2 |
10.0 |
8.6 |
1.5 |
4.1 |
11.5 |
13.5 |
7.2 |
| Musculoskeletal system |
20,564 |
8.5 |
2.0 |
8.5 |
8.5 |
2.9 |
6.9 |
12.3 |
10.0 |
4.7 |
| Genitourinary System |
18,469 |
7.6 |
1.5 |
8.0 |
7.2 |
3.2 |
6.7 |
8.6 |
8.7 |
6.8 |
| Pregnancy, birth and puerperium |
14,069 |
5.8 |
-3.1 |
- |
11.9 |
0.0 |
31.7 |
0.3 |
- |
- |
(*)The percentage has been calculated on the total number of hospitalizations
ICD -10 : International Classification of Diseases, 10th version
Date November 19, 2025
Source: Eustat. Hospital discharge statistic
The order of the most common illness groups and specific causes varied significantly with age
The illnesses causing hospital admissions varied according to the age group of the population admitted. Standing out among the population under 15 years of age were respiratory conditions, primarily hypertrophy of the tonsils and adenoids, while among those aged 15 to 44, in addition to childbirth and pregnancy care, digestive conditions (diseases of the appendix) and trauma and injuries (anterior cruciate ligament knee sprains and leg fractures) were predominant. In the 45-64 age group, digestive conditions continued to predominate, albeit with other types of ailments: cholelithiasis (gallstones) among women and inguinal hernias among men. Diseases of the musculoskeletal system (osteoarthritis of the hip and knee) and tumours (breast tumours in women and prostate tumours in men) also became more prevalent.
Among people aged 65 and over, circulatory diseases were the most common. The most noteworthy of these were cardiac conduction disorders and arrhythmias, cerebrovascular diseases (such as cerebral infarctions) and hypertensive disease (more prevalent in the 80 and over age group). They were followed by respiratory conditions, which had a greater impact among people aged 80 and over (especially pneumonia), and then digestive and tumour conditions (bladder and prostate), which were more common in the 65-79 age group.
The average length of stay dropped to 5.4 days
People admitted to hospital accounted for 1,303,743 stays (i.e. the number of days from the date of admission of the patient to the date of discharge), representing an increase of 0.8% compared to 2023, with the average length of stay standing at 5.4 days (5.5 in 2023). For men, it was 5.6 days, and for women, 5.2 days, and by age group, the longest average stays were recorded at the beginning and end of the life cycle: under 1 year old (7.4 days) and 80 years old and over (6.4 days).
In terms of illness groups, those that resulted in the longest stays were mental health and behavioural disorders (14.3 days), together with illnesses originating in the perinatal period (8.9 days) and infectious and parasitic diseases (8.4 days).
Methodological note
For reasons of comparability with Spanish and international statistics, the hospital admissions mode only takes into account admissions with a stay equal to or greater than 1 day, that is, admissions with 0 days are not counted. The length of stay is calculated as the number of days between the date of admission and the date of discharge, without taking into account the time of admission or discharge.
Admissions to medium and long-stay and psychiatric hospitals are not included.
For further information:
Eustat - Euskal Estatistika Erakundea/Basque Statistics Institute
C/ Donostia-San Sebastián, 1 01010 Vitoria-Gasteiz
Press Service: servicioprensa@eustat.eus Tel.: 945 01 75 62