Press Release 30/09/2024
POPULATION AND HOUSING CENSUS. EDUCATION. 2023
In the Basque Country, 43.3% of the population over 15 years old had completed higher education in 2023
One in ten people aged 16 and over were still in education
In 2023, 43.3% of the population aged 16 and over residing in the Basque Country had completed higher education, whether university studies or vocational training, according to Eustat data. This group represented 821,517 people and increased by 1 tenth of a percentage point in respect of 2022. Meanwhile, the percentage of the population that had completed compulsory education or lower was 36.2% (685,830 people), 0.3 percentage points less than in 2022.
Population aged 16 and over in the Basque Country by level of education attained. 2022-2023


| | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 (%) | 2022 (%) |
| | | | | |
| Level of training achieved | 1.895.243 | 1.879.375 | 100 | 100 |
| | | | | |
| A.First stage of secondary and lower education (level 0-2) | 685.830 | 686.009 | 36,2 | 36,5 |
| 0.Less than primary | 30.724 | 31.983 | 1,6 | 1,7 |
| 1. Primary education | 192.741 | 200.395 | 10,2 | 10,7 |
| 2.Low secondary education: up to ESO and equivalent | 462.365 | 453.631 | 24,4 | 24,1 |
| | | | | |
| B.Second stage of secondary education and non-tertiary post-secondary education (level 3-4) | 387.896 | 382.308 | 20,5 | 20,3 |
| 3.Upper secondary education: Baccalaureate, intermediate vocational training and equivalent | 376.000 | 370.307 | 19,8 | 19,7 |
| 4.Non-tertiary post-secondary education: level 3 professional certificates and equivalent | 11.896 | 12.001 | 0,6 | 0,6 |
| | | | | |
| C.Higher education (including doctorate)(level 5-8) | 821.517 | 811.058 | 43,3 | 43,2 |
| 5.Higher vocational education and equivalents | 291.217 | 291.103 | 15,4 | 15,5 |
| 6.University degrees, diplomas and equivalents | 193.565 | 186.876 | 10,2 | 9,9 |
| 7.Bachelor's degrees, double degrees and master's degrees | 314.962 | 311.523 | 16,6 | 16,6 |
| 8.PhD level or equivalent | 21.773 | 21.556 | 1,1 | 1,2 |
Date September 30, 2024
Source: Eustat. Population and housing census. Education
According to the National Classification of Education (CNED-A), the first education group corresponds to the first stage of secondary education or lower, ranging from basic and compulsory education to lower levels. 36.2% of the population aged 16 and over belonged to this group, a drop of 0.3 points compared to the previous year. This included people who had not completed primary school level education (1.6%), people who had completed primary education (10.2%) and people who had completed the first stage of secondary education (24.4%), which includes qualifications equivalent to Compulsory Secondary Education, Basic General Education and Lower Secondary Education, among others, as well as some vocational training.
The second group corresponds to secondary education and post-secondary non-higher education, which comprised 20.5% of the population aged 16 and over, an increase of 0.2 percentage points compared to 2022. This level of education includes upper secondary education and basic and intermediate level vocational training. The third group, higher education, accounted for 43.3% of the population, with another increase of 0.1 points in respect of the previous year. Within this group, 15.4% corresponded to advanced level vocational training, with 291,217 people.
Plentzia-Mungia and Estribaciones del Gorbea had the highest proportion of people with higher education, together with San Sebastián
An analysis of the level of education attained by the population aged 16 and over, taking into account the disaggregation by province, revealed small percentage differences. Álava registered the highest proportion of people with a level of education belonging to group A, which corresponds to the first stage of secondary education or lower, with 37.3% of the population aged 16 and over. This figure was slightly higher than the 36.4% recorded in Bizkaia and the 35.3% in Gipuzkoa.
Population aged 16 and over in the Basque Country by the level of education achieved according to historical territory (%). 2022-2023
| | Basque Country | Araba / Álava | Bizkaia | Gipuzkoa |
| | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Level of training achieved | 1.895.243 | 1.879.375 | 283.294 | 280.449 | 994.166 | 986.633 | 617.783 | 612.293 |
| A.First stage of secondary and lower education (level 0-2) | 36,2 | 36,5 | 37,3 | 37,4 | 36,4 | 36,8 | 35,3 | 35,7 |
| B.Second stage of secondary education and non-tertiary post-secondary education (level 3-4) | 20,5 | 20,3 | 21,6 | 21,5 | 20,0 | 19,8 | 20,8 | 20,7 |
| C.Higher education (including doctorate)(level 5-8) | 43,3 | 43,2 | 41,1 | 41,1 | 43,6 | 43,4 | 43,9 | 43,7 |
Date September 30, 2024
Source: Eustat. Population and housing census. Education
As for group B, which includes the second stage of secondary education and post-secondary non-higher education, Álava once again had the highest percentage of 21.6%, compared to 20.8% in Gipuzkoa and 20% in Bizkaia. However, in the case of group C, which represents higher education, Gipuzkoa recorded the highest proportion with 43.9%, followed by Bizkaia with 43.6%, while Álava was slightly below this, with 41.1%.
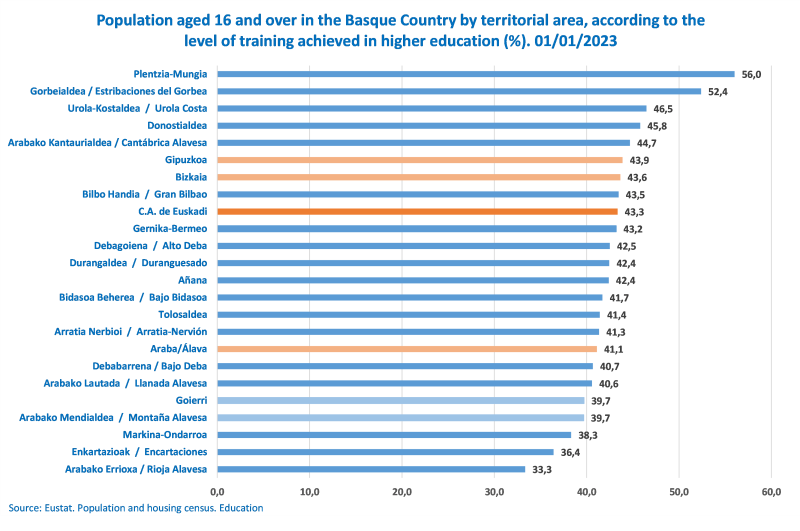
Differences in the level of higher education were more pronounced at the regional level. Plentzia-Mungia and Estribaciones del Gorbea stood out as the regions where more than half of the population had completed higher education, with 56% and 52.4%, respectively. These figures exceeded the average for the Basque Country by 12.7 and 9 percentage points. At the other end of the scale, the regions of Rioja Alavesa, with 33.3%, and Encartaciones, with 36.4%, registered the lowest percentages, with around a third of the population having completed higher education.
Among the Basque capitals, San Sebastián recorded the largest proportion of people with higher education (51%), followed by Bilbao with 47.6% and Vitoria-Gasteiz with 40.5%. This order follows the trend seen at the provincial level, where Gipuzkoa also came out on top in terms of the proportion of the population with higher education.
44% of men and 42.8% of women had completed higher education
Among men and women aged 16 and over, the largest group was higher education, with 44% in the case of men and 42.8% in that of women; next was the first stage of secondary education or lower, with a higher relative weight among women (38.2%) than men (34%); and, lastly, the second stage of secondary education and post-secondary non-higher education was more common among men (22.1%) than women (19%). By province and in terms of higher education, women residing in Álava stood out for having a higher relative value than men, 40.8% compared to 41.4%.
Population aged 16 and over in the Basque Country by level of education attained according to historical territory and sex (%). 2023
| | Basque Country | Araba / Álava | Bizkaia | Gipuzkoa |
| | Total | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Level of training achieved | 1.895.243 | 910.604 | 984.639 | 283.294 | 137.915 | 145.379 | 994.166 | 473.692 | 520.474 | 617.783 | 298.997 | 318.786 |
| GROUP A | 685.830 | 34,0 | 38,2 | 105.785 | 36,1 | 38,5 | 361.778 | 33,8 | 38,7 | 218.267 | 33,2 | 37,3 |
| GROUP B | 387.896 | 22,1 | 19,0 | 61.068 | 23,1 | 20,1 | 198.454 | 21,5 | 18,5 | 128.374 | 22,4 | 19,3 |
| GROUP C | 821.517 | 44,0 | 42,8 | 116.441 | 40,8 | 41,4 | 433.934 | 44,6 | 42,7 | 271.142 | 44,4 | 43,4 |
Date September 30, 2024
Source: Eustat. Population and housing census. Education
One in ten people aged 16 and over were still in education and, of these, almost half were pursuing higher education
In 2023, 11.1% of the population aged 16 and over in the Basque Country, equivalent to 210,699 people, were enrolled in some level of education. Almost half of this group of students, 49.6% (a total of 104,630 people), were pursuing higher education. 40.4%, 85,083 people, were at the level of secondary education and post-secondary non-higher education. 7.2%, i.e. 15,151 people, were at the level of first stage of secondary education or lower. Lastly, 2.8%, equivalent to 5,836 people, were enrolled in non-formal education for adults.
If we look at the student population aged 16 and over as a whole and disaggregated by gender, we can see that there was a higher proportion of women, representing 52.5%, in comparison to men, accounting for 47.5%. This difference was seen at all levels of ongoing education. At the primary school level, women represented 53.5%, a difference of 7 percentage points compared to men.
If we look at men and women separately, the distributions were similar, although among men, there was a higher proportion of students in both group C, Higher education (+1.2 points), and group B, Second stage of secondary education and post-secondary non-higher education (+0.4 points); while among women, there was a higher proportion of students in group A, First stage of secondary education or lower (-0.2 points), and, in particular, non-formal education (-1.3 points).
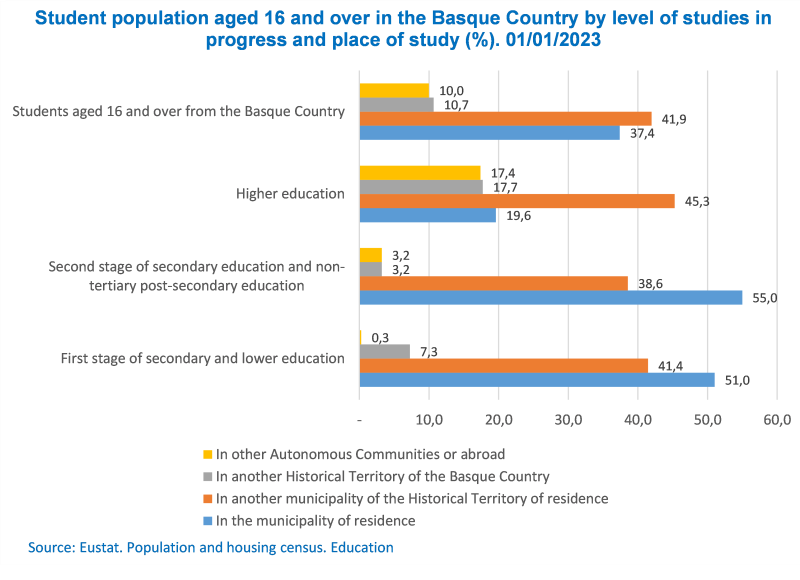
The Basque population that pursued higher education primarily moved to another municipality in the same province
In 2023, more than half of students in the first stage of secondary education or lower, as well as in secondary education and post-secondary non-higher education, studied in their home province, with percentages of 51% and 55%, respectively. As for the population aged 16 and over in the Basque Country that pursued university studies or advanced level vocational training, 45.3% (47,390 people) moved to a municipality within their home province. At this level of education, it is worth highlighting that 17.4% of students attended centres outside the Basque Country or abroad, a trend not seen at other education levels.
For further information:
Eustat - Euskal Estatistika Erakundea / Basque Statistics Institute
C/ Donostia-San Sebastián, 1 01010 Vitoria-Gasteiz
Press Service: servicioprensa@eustat.es Tel.: 945 01 75 62