Press Release 21/03/2024
HOSPITAL MORBIDITY STATISTICS. 2022
Hospital admissions in the Basque Country increased by 4.1% in 2022
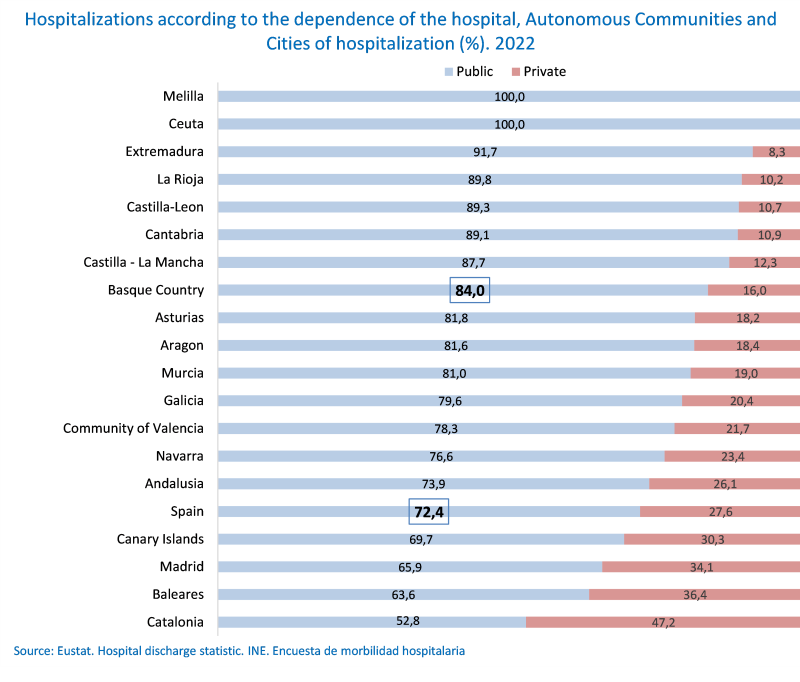
84% of admissions were treated in public hospitals, almost 12 percentage points above the Spanish average and more than 30 points higher than in Catalonia
Hospitals in the Basque Country recorded a total of 243,427 admissions in 2022, up 4.1% on the previous year, according to Eustat data, which represented 5.1% of the total for Spain as a whole. 84% of cases were treated in public hospitals, nearly twelve percentage points more than at national level (72.4%) and ahead of eleven of the seventeen autonomous regions, including Catalonia (52.8%), the Balearic Islands (63.6%), Madrid (65.9%) and the Canary Islands (69.7%), which also had lower public care figures than the Spanish average.
�
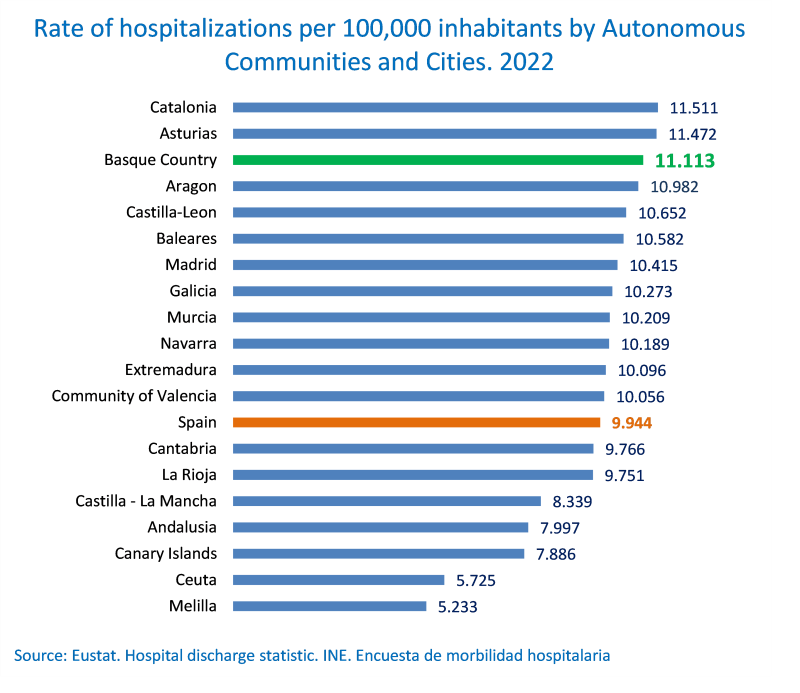
The Basque Country ranked among the Autonomous Regions with the highest hospital morbidity rates in Spain
The Basque Country registered a rate of 11,113 hospitalisations per 100,000 inhabitants, placing it above the national average (9,944) and third among the Autonomous Regions with the highest hospitalisation rates, after Catalonia (11,511) and Asturias (11,472).
By sex, the proportion of men (50.9%) was slightly higher than that of women (49.1%), whilst nationally it was higher for women (51.6%). If pregnancy, childbirth and postnatal cases were not taken into account, the percentage of women would drop to 45.8% in the Basque Country (47.5% in Spain).
53% of people admitted to Basque hospitals were aged 65 and over, while in Spain this figure stood at 48%
The number of people admitted to hospital aged 65 and over represented 53.2% of hospitalisations in the Basque Country in 2022 (51.1% in 2021), five percentage points up on the figure for Spain (47.9%). Within this group, cases involving people aged 85 and over saw the greatest increase (11.3%), but it was the 65-84 age group that accounted for the highest number of admissions (37.3% and 33.7% in Spain), followed by the 45-64 age range (24.6%) and those aged 85 and over (15.9%).
There was a rise in the number of hospital admissions due to respiratory diseases, making them the third leading cause of hospitalisation in the Basque Country, behind circulatory and digestive diseases
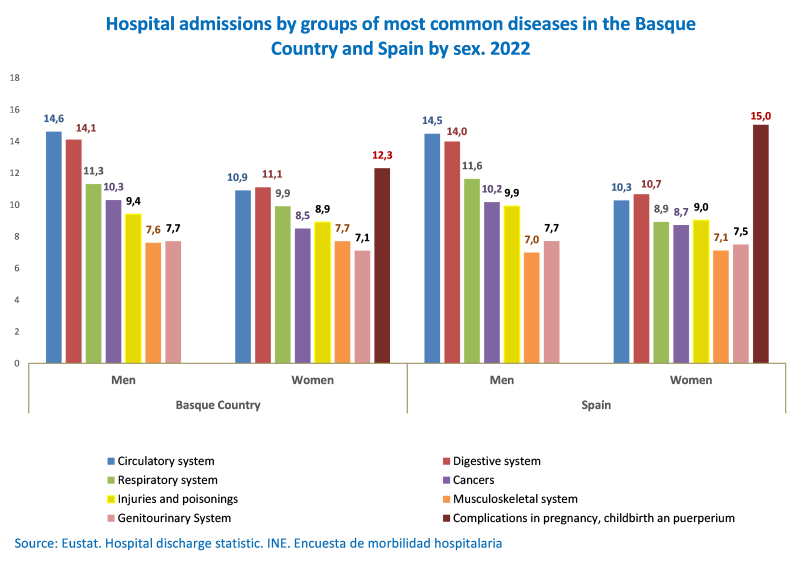
Diseases of the circulatory system (12.8%) and the digestive system (12.6%) continued to be the main causes of hospital admissions in the Basque Country, as was the case in Spain. Between them, they accounted for 25.4% of hospitalisations (24.6% in Spain).
Compared to 2021, hospital admissions due to respiratory diseases increased by 36.3% in 2022, making them the third most common cause of hospitalisation in the Basque Country (10.6%), as well as in Spain (10.2%), followed by tumours (9.4%) and injuries and poisoning (9.2%). Meanwhile, the group of hospital stays associated with pregnancy, childbirth and postnatal care saw the greatest difference between hospitalisations in the Basque Country and the rest of Spain (6.1% and 7.8%, respectively).
The number of hospitalisations due to diseases of the circulatory, digestive and respiratory systems was higher among men
Excluding cases of pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum care, which accounted for the highest number of hospital admissions among women (12.3%), the three main causes of hospitalisation were the same for both sexes, although there were some differences: circulatory diseases were the leading cause among men and digestive diseases the leading cause among women, and the number of hospital admissions was higher among men for the aforementioned two groups, together with respiratory diseases.
Within the most common disease groups, the specific causes behind most hospitalisations related to the circulatory system were cerebral infarction and heart failure for both sexes; for digestive diseases, the causes were cholelithiasis (gallstones) for women and inguinal hernia for men. Of particular note in the respiratory diseases group were pneumonia and other chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPDs), which were more common among men. As regards tumours, bladder, bronchial, lung and prostate tumours, with a high prevalence among men, were responsible for the greatest number of hospitalisations.
The average length of stay in hospital was higher for men than for women
The total number of days that people spent in hospital in the Basque Country came to 2,045,883, a drop of 6.3% compared to 2021. The average length of stay stood at 8.4 days (8.1 in Spain) and was higher among men (9.3 days) than women (7.5 days); in the case of men, it surpassed the Spanish average (8.8 days).
Hospitalisations, days of stay and average stay in hospitals in the Basque Country by groups of most frequent diseases. 2022


| | Hospitalisations | Days of stay | Average stay |
| | Number | % | Number | % | Total | Men | Women |
| TOTAL | 243.427 | 100 | 2.045.883 | 100 | 8,4 | 9,3 | 7,5 |
| Circulatory system | 31.094 | 12,8 | 241.728 | 11,8 | 7,8 | 7,7 | 7,9 |
| Digestive system | 30.673 | 12,6 | 157.199 | 7,7 | 5,1 | 5,0 | 5,3 |
| Respiratory system | 25.840 | 10,6 | 169.640 | 8,3 | 6,6 | 6,0 | 7,2 |
| Tumors | 22.954 | 9,4 | 156.303 | 7,6 | 6,8 | 7,1 | 6,4 |
| Trauma, poisoning and other consequences of external causes | 22.353 | 9,2 | 147.014 | 7,2 | 6,6 | 6,6 | 6,6 |
| Musculoskeletal system | 18.609 | 7,6 | 82.407 | 4,0 | 4,4 | 4,3 | 4,6 |
| Genitourinary System | 17.950 | 7,4 | 77.750 | 3,8 | 4,3 | 4,3 | 4,4 |
| Pregnancy, birth and puerperium | 14.752 | 6,1 | 46.107 | 2,3 | 3,1 | . | 3,1 |
| Abnormal clinical symptoms and findings | 10.806 | 4,4 | 54.316 | 2,7 | 5,0 | 5,1 | 4,9 |
| Codes for special purposes (COVID-19) | 9.229 | 3,8 | 76.139 | 3,7 | 8,3 | 8,6 | 7,9 |
| Mental and behavioural disorders | 7.572 | 3,1 | 591.154 | 28,9 | 78,1 | 98,7 | 56,3 |
| Certain infectious and parasitic diseases | 6.282 | 2,6 | 57.918 | 2,8 | 9,2 | 9,5 | 8,9 |
The percentage has been calculated on the total number of hospitalizations and stays
ICD -10 : International Classification of Diseases, 10th version
Date March 21, 2024
Source: Eustat. Hospital discharge statistic
The mental health and behavioural disorders group stood out from the other groups of illnesses due to the prolonged length of hospital stays for some pathologies (schizophrenia and personality and behavioural disorders). This group alone accounted for 28.9% of all hospital stays and the average length of stay stood at 78.1 days (98.7 for men and 56.3 for women).
With regard to the other groups of illnesses, diseases of the circulatory system (11.8%), respiratory system (8.3%), digestive system and tumours (7.7% and 7.6%, respectively) accounted for the greatest number of hospital stays, while perinatal conditions and infectious diseases recorded the highest average lengths of stay (10.3 days and 9.2 days).
Methodological note
This statistical operation has been carried out in collaboration with the National Institute of Statistics-INE.
These statistics cover acute care hospitals, medium and long-stay hospitals and psychiatric hospitals.
For reasons of comparability with Spanish and international statistics, the hospital admissions mode only takes into account admissions with a stay equal to or greater than 1 day, that is, admissions with 0 days are not counted. The length of stay is calculated as the number of days between the date of admission and the date of discharge, without taking into account the time of admission or discharge.
For further information:
Eustat - Euskal Estatistika Erakundea / Basque Statistics Institute
C/ Donostia-San Sebastián, 1 01010 Vitoria-Gasteiz
Press Service: servicioprensa@eustat.eus Tel.: 945 01 75 62