Press Release 29/11/2019
HOSPITAL MORBIDITY STATISTICS. 2018
The number of hospital admissions due to respiratory diseases was up 8.8% in the Basque Country in 2018
There were also 79,241 outpatients admitted, 5.4% more than in 2017
A total of 235,634 people were admitted to acute care hospitals in the Basque Country (not including medium and long-stay hospitals and psychiatric hospitals) in 2018, which was an increase of 1.2% compared to the previous year, according to Eustat data. The main causes of hospital admissions were digestive, respiratory and circulatory diseases, which as a whole accounted for 38.8% of admissions. Compared to 2017 of particular note is the increase in admissions caused by respiratory diseases (8.8%), well above the 1.3% rise in admissions caused by circulatory diseases, and the fluctuation in those caused by digestive diseases, which decreased by 0.3%. In addition, 79,241 people were treated as outpatients (+5.4%); in this case the main reason for treatment was cataract surgery.
In terms of hospital ownership, 83.3% of admissions were registered in public hospitals and 16.7% in private hospitals; in the latter there was a different treatment pattern, as musculoskeletal problems (18.5%) were the most treated pathologies.
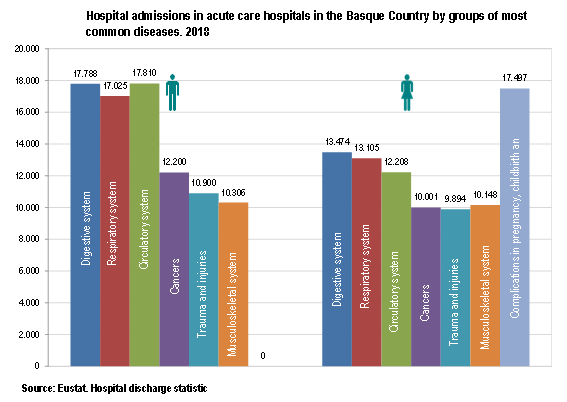
Although the proportion of hospital admissions for men (50.7%) was similar to that for women (49.3%), if we exclude cases of care for childbirth, pregnancy and postnatal issues, which, in general do not constitute a health problem, this percentage stood at 54.8% for men, nearly 10 percentage points above that for women (45.2%).
People aged 65 and over attended hospitals more frequently and represented almost half of all admissions (49%) and, amongst them, 44.7% corresponded to people aged 80 and over. These figures are very similar to those from the previous year.
Of the total number of admissions, those caused by diseases of the digestive system (13.3%) were the most common, followed by, in joint second place, diseases of the respiratory system (12.8%), with an increase of 8.8% compared to 2017, and circulatory diseases (12.7%); next came tumours (9.4%), trauma and injuries, and with a similar weighting, diseases of the musculoskeletal system (8.8% and 8.7% respectively). Care for pregnancy, childbirth, and postnatal issues decreased by 5.3% compared to 2017, accounting for 7.4% of hospital admissions.
Amongst women, excluding cases linked to maternity (15.1%), treatment was received for, in first place, diseases of the digestive system (11.6%), followed by those of the respiratory system (11.3%) and circulatory system (10.5%) in second and third place.
Amongst men, the three main causes coincided with those of women, although the proportion of cases was greater. Diseases of the circulatory system and those of the digestive system were in joint first place (both with 14.9%), followed by respiratory diseases (14.2%).
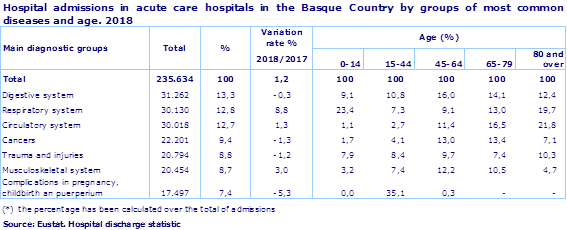
Additionally, hospital admissions are closely related to age: in the 0-14 age group respiratory and perinatal diseases were the most common; in the 15-44 age group admissions linked to pregnancy, childbirth and postnatal issues predominated, with 35.1%; as age increases other pathologies are predominant: digestive diseases and tumours in the 45-64 age group, circulatory diseases amongst individuals in the 65-79 age group and circulatory and respiratory diseases in those aged 80 and above.
If pregnancy, childbirth and postnatal care are excluded, the average age of individuals admitted to hospital was 62 years. This figure was higher (72 years) for circulatory diseases. The average age of hospital admission for men was below that of women, except in the case of tumours and diseases affecting the genitourinary system; the greatest difference occurred in hospital admissions due to trauma and injuries (54 years, compared to 67 years for women).
The average length of hospital stays was 5.7 days, identical to that of 2017; the longest stays were for mental disorders (13.9 days), followed by perinatal diseases (11.5 days) and infectious diseases (8.7 days).
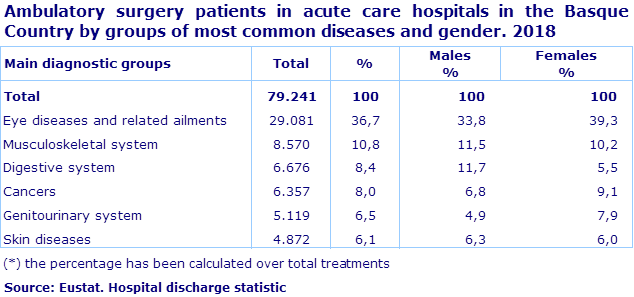
Cataracts and eye diseases accounted for 36.7% of outpatient surgery
Outpatient surgery, where patients are admitted, treated and discharged on the same day, recorded 79,241 admissions (5.4% more compared to 2017). The group of eye diseases was the most common, accounting for 36.7% of cases treated, of which 88.7% were carried out in public hospitals and 11.3% in private hospitals, with cataracts being the most treated pathology.
In second place were diseases of the musculoskeletal system (10.8%), where 56.4% of procedures were carried out in private hospitals, with the most frequent being knee disorders, in men, and bunions, in women.
Methodological note
For reasons of comparability with Spanish and international statistics, the hospital admissions mode only takes into account admissions with a stay equal to or greater than 1 day, that is, admissions with 0 days are not counted. The length of stay is calculated as the number of days between the date of admission and the date of discharge, without taking into account the time of admission or discharge.
For further information:
Eustat - Euskal Estatistika Erakundea / Basque Statistics Institute
C/ Donostia-San Sebastián, 1 01010 Vitoria-Gasteiz
Press Service: servicioprensa@eustat.es Tel: 945 01 75 62