Press Release 14/03/2018
Acute care hospitals in the Basque Country registered 242,171 admissions in 2016
In addition, 76,098 individuals underwent outpatient surgery
Of the total of 242,171 hospital admissions registered in 2016 in acute care hospitals in the Basque Country, almost 40% were for digestive, circulatory and respiratory diseases, according to Eustat data. In addition, acute care hospitals treated 76,098 individuals as outpatients; in this case the main reason for treatment was eye diseases.
As for the conventional mode of hospital admission (with bed occupancy), 83% of individuals were treated in public hospitals and 17% in private hospitals; in the latter there was a different treatment pattern, as musculoskeletal problems (18%) were the most treated pathologies.
The proportions of hospital admissions were similar for women (50.3%) and men (49.7%). However, if admissions due to pregnancy or childbirth, which, in general, do not constitute a health problem, are not taken into account, these percentages stood at 54.3% for men and 45.7% for women.
Older people attend hospitals more frequently and represent almost half of all admissions: 47.1% of admitted individuals were aged 65 or over and 20.8% were in their eighties.
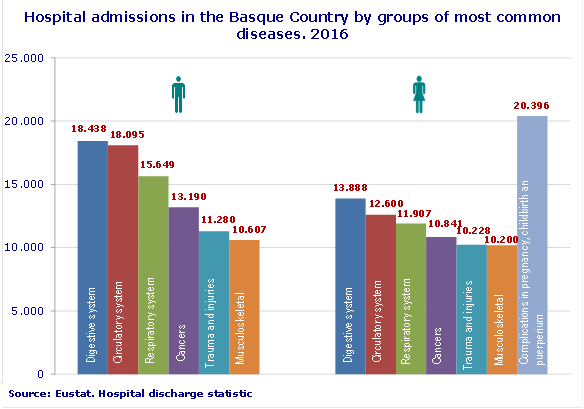
Of the total of hospital admissions, those resulting from diseases of the digestive system (13.3%) were the most common, followed by those of the circulatory system (12.7%), respiratory system (11.4%), tumours (9.9%) and trauma and injuries (8.9%).
Amongst women, excluding care for pregnancy, childbirth and postnatal issues (16.7%), treatment was received for, by order of frequency, diseases of the digestive system (11.4%), with gallstones being the most diagnosed pathology, followed by the circulatory system (10.3%), with heart failure the most common pathology, and finally the respiratory system (9.8%), with pneumonia being the most prominent disease.
Amongst men, the three main reasons for treatment coincide with those of women, although, within diseases of the digestive system, the most common were inguinal hernias.
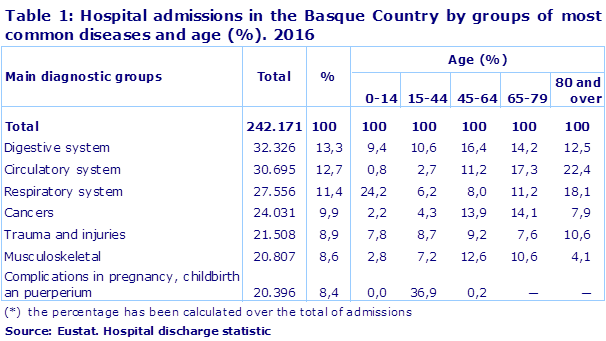
Additionally, hospital admissions are closely related to age: in the 0-14 age group respiratory and perinatal diseases were the most common; in the 15-44 age group 37% of admissions were connected with pregnancy, childbirth and postnatal issues; as age increases other pathologies are predominant: digestive diseases and tumours in the 45-64 age group, and circulatory diseases amongst individuals aged 65 and over.
If pregnancy, childbirth and postnatal care are not considered, the average age of individuals admitted to hospital was 61 years. This figure was higher (72 years) for circulatory diseases. Except in the case of tumours, due to the incidence of breast cancer in women, the average age of hospital admission for men was below that of women, and the greatest difference occurred in hospital admissions due to trauma and injuries (53 years, compared to 66 years for women).
Individuals admitted to hospital that died accounted for 3.1% of hospital admissions. The main causes of death were circulatory diseases (21.8%), tumours (21.1%) and respiratory diseases (17.7%).
The average stay in hospital stood at 5.3 days. The longest stays were for mental disorders (13.2 days), followed by perinatal diseases (10.3 days), infectious diseases (8.6 days) and tumours (6.8 days).
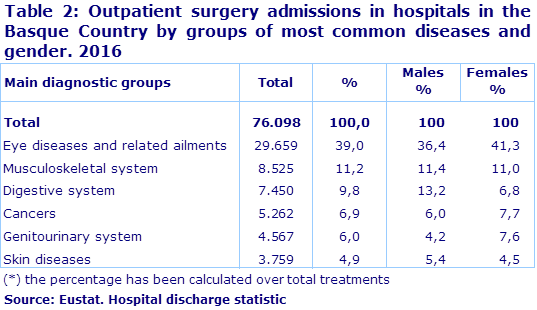
Cataracts and eye diseases accounted for 39% of outpatient surgery
Outpatient surgery, where patients are admitted, treated and discharged on the same day, is gradually substituting conventional hospital admission.
76,098 admissions were registered for this type of medical treatment, of which 39% corresponded to the group of eye diseases, with cataracts being the most treated pathology, especially amongst women aged 65 to 79.
In second place were diseases of the musculoskeletal system (11.2%), within which the most frequent interventions were meniscus disorders, in men, and bunions, in women.
Pathologies of the digestive system (9.8%) occupied third place. These affected men (13.2%) more than women (6.8%). Inguinal hernias were the most treated ailment.
Methodological note:
The data refers to hospitals providing acute care.
In 2016 there were changes in the registration of hospital admissions in the Basque Country, the source of these statistics, by virtue of the Health Department Order of 13 October 2015, which incorporated new variables into the Minimum Basic Hospital Admission Data Set, under the heading of Minimum Basic Specialised Care Data Set; the variable "type of contact" enables hospital admissions (conventional) to be separated from outpatient surgery admissions, unlike the previous version where all hospital admissions were dealt with jointly. Also in 2016, hospitals started codifying using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10) instead of the ICD 9. For these reasons it is not possible to make direct comparisons with the previous year.
For further information:
Eustat - Euskal Estatistika Erakundea / Instituto Vasco de Estadística
C/ Donostia-San Sebastián, 1 01010 Vitoria-Gasteiz
Press Service: servicioprensa@eustat.eus Tel: 945 01 75 62