Press Release 09/03/2017
56% of female students chose to continue their studies at upper secondary level, compared to 40% of their male counterparts
32% of students received some type of grant or public aid for their studies, reaching 44% for compulsory education
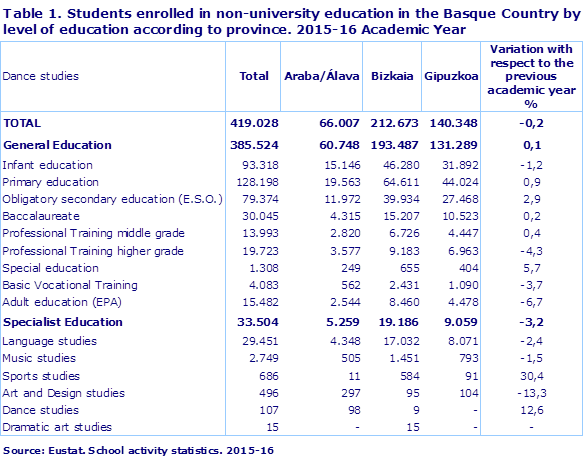
There were 419,028 students enrolled in non-university education in the Basque Country over the 2015-16 academic year, which signified a decrease of 0.2% with respect to the previous academic year, according to data prepared by Eustat. 92% of them took General Education courses, which saw an increase of 0.1%, while the remaining 8% were enrolled in Specialised Education, which fell by 3.2%.
By province, half of all students studied in Bizkaia, 34% in Gipuzkoa and 16% in Álava. A similar distribution was seen in General Education courses, but not in Specialised Education, where a provincial specialisation was observed in Sports Education, with a concentration of students (85%) in Bizkaia, in Art and Design (60%) in Álava, and in Dance and Dramatic Art, which was only offered in Álava and Bizkaia.
With regard to the governing body, in General Education, students were distributed equally between public and private centres, except for Professional Training studies where six of every ten enrolments was at a public centre, and Adult Education, where almost all enrolments were at public centres. For Specialised Education, the majority of students were registered at public centres: 100% in Languages, Dance and Dramatic art, and around 70% in the other courses.
In General Education, there were 320 more enrolments, an increase of 0.1% on the previous academic year. The greatest increase was seen in Compulsory Secondary Education which was up 2.9%. On the other hand, Specialised Education saw an increase of 6%.
It is worth mentioning that after 18 years of continued increase, the enrolment levels in Infant Education dropped for a third consecutive year (-1.2%), reaching levels not seen since 2009-2010, and with a loss of 3,395 students over the past three years. Higher-level Vocational Training also registered a drop in student numbers (-4.3%) after seven years of increases.
In Specialised Education, student numbers were down by 3.2% across the board, except in Dance, which registered an increase of 13%. The greatest decreases in enrolments were seen in Sports Studies (-30%) and Art and Design (-13%).
While six out of ten female students chose to continue their studies at upper secondary level, six out of ten male students opted for Vocational Training
On completion of compulsory education, half of all students elected to continue their academic studies, while the other half opted for vocational training. Gender, however, had a decisive influence on this choice. Thus, while 56% of female students enrolled in Upper Secondary Education (Baccalaureate), 60% of their male counterparts opted for vocational training.
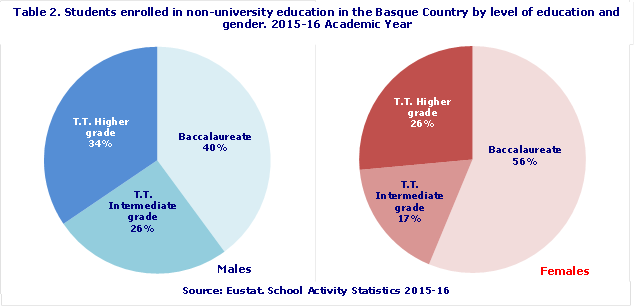
In Upper Secondary Education (Baccalaureate), the modalities chosen were divided between Humanities or Social Sciences (44%) and Science or Technology (52%), with just 4% of students enrolling in Arts. From a gender perspective, 60 out of 100 male students opted for Science and Technology, compared to 46 out of 100 female students.
The following courses constituted 44% of enrolments in Vocational Training: Mechanical Manufacturing (13%), Electricity and Electronics (10%), Healthcare (10%) and Administration and Management (10%). Gender also played a decisive role in the choices made in Vocational Training, with 59% of female students enrolled electing to study one of the following courses: Healthcare (22%), Socio-Cultural and Community Services (20%) and Administration and Management (17%). On the other hand, half of male students opted for: Mechanical Manufacturing (19%), Electricity and Engineering (16%) and Information & Communications (11%).
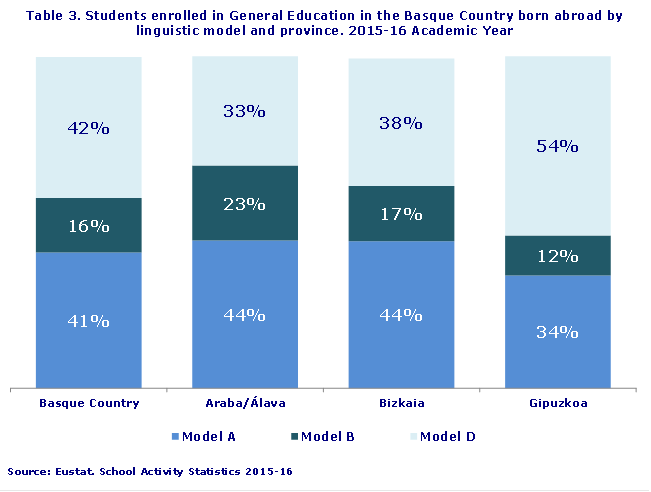
In Gipuzkoa, the majority of foreign students followed model D
In the 2015-16 academic year, 31,267 foreign students (8% of the total) were enrolled in General Education in the Basque Country. While the proportion of foreign students in Bizkaia and Gipuzkoa was similar (7% and 8%, respectively), their presence was higher in Álava (11%).
With regard to the linguistic integration of foreign students, Gipuzkoa topped the list with the highest percentage of foreign students enrolled in model D (54%) followed by Bizkaia (38%) and Álava (33%).
The courses with the highest proportion of foreign students enrolled were the Basic Vocational Training Programmes (28%) and Adult Education (42%). The proportion fluctuated between 5% and 13% for the other courses.
32% of students were awarded some kind of grant
In the 2015-16 academic year, the amount of grants and aid awarded by the Public Administration of the Basque Country amounted to 55 million euros, and benefited a total of 127,431 students, 31.8% of the total.
The highest number of grants were awarded in compulsory education. 50% of students in Basic Vocational Training were awarded grants, followed by 44% of those in Primary Education and Secondary and Specialised Education, with 42% and 43%, respectively.
It should also be mentioned that 29% of students in Upper Secondary Education and 16% of those in Vocational Training were awarded grants. However, in specialised education the number of students receiving grants was lower, just 1% of the total.
For further information:
Eustat - Euskal Estatistika Erakundea / Instituto Vasco de Estadística
C/ Donostia-San Sebastián, 1 01010 Vitoria-Gasteiz
Press Service: servicioprensa@eustat.eus Tlf: 945 01 75 62
Further press releases on School activity statistics of the Basque Country
Database on School activity atatistics of the Basque Country