Press Release 17/05/2016
The Basque Country is in fifth place in the Gender Equality Index ranking of the countries of the European Union
The highest values in gender equality were reached in the dimensions of Health, Money and Employment
The Gender Equality Index (GEI) in the Basque Country was 58.5 points in 2012, slightly higher than Belgium, which placed it in fifth position in the Gender Equality Index ranking of the countries of the European Union, according to EUSTAT data.
The Basque Country comes behind the Scandinavian countries (Sweden, Finland) and some Northern European countries (Denmark, Netherlands), but in front of the remaining 24 members of the European Union and well in front of the European average.
With 96.2 points, the dimension of Health comes closest to total equality between persons of different genders, although it must be taken into account that, in this case, the slight inequality is the result of the better situation of women. At the other extreme, the greatest inequality is found in the dimension of Time, with a partial indicator of 39.2 points out of 100.

With the publication of the first edition of the Gender Equality Index in the Basque Country, Eustat takes a further step towards its objective of creating statistical information that allows the gender perspective to be introduced into the analysis of the distinct aspects - political, social, cultural, economic, etc.- of Basque society.
The Gender Equality Index is a synthetic indicator that summarises in a dimensionless scale, on which 0 signifies total inequality and 1 signifies total equality, the inequalities that still exist between men and women in a series of significant aspects that affect their welfare and their personal development.
It has been created using the methodology of the European Institute for Gender Equality (EIGE), which enables advances in gender equality in the Basque Country to be compared with advances made in the European Union and its 28 member countries. The methodology comprises 26 indicators structured hierarchically into six dimensions that are in turn divided into 12 subdimensions.
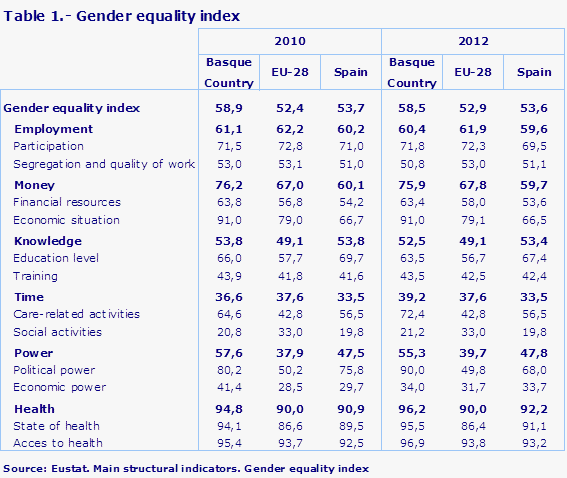
Between 2010 and 2012 the Gender Equality Index has improved in the Health and Time dimensions and worsened in the others
Between 2010 and 2012 the gender equality indicators have improved in the areas of health and time, but have worsened in the others, especially in the power dimension, where the indicator has lost 2.3 points. This fall is a result of trends in the area of economic power; in terms of political power, the indicator points to an improvement in equality between men and women in the Basque Country, from an already higher level in 2010.
Amongst the EU-28 countries, the Basque Country occupies first place in the dimension of Health and fourth place in that of Power
In the Basque Country the highest values in gender equality are obtained in the health, money and employment dimensions. Nevertheless, the relative position of the Basque Country in comparison with the countries of the European Union in 2012 is better in the health and power dimensions, in which it occupies first and fourth place respectively. Regarding the EU-28 average, the Basque Country obtained a more favourable value in all dimensions, except in employment, where the value is 1.5 points less.
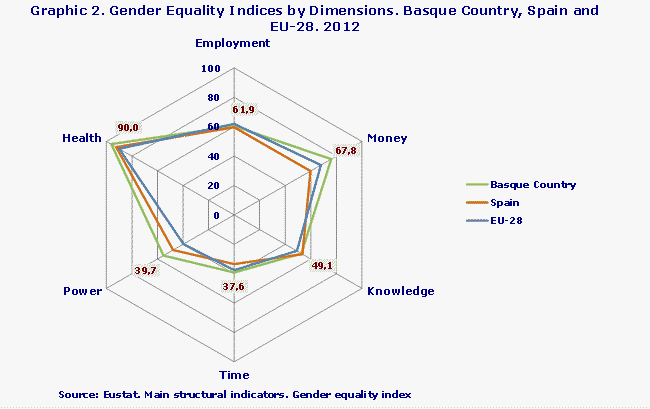
The Gender Equality Index in the Basque Country is almost 5 points ahead of that of Spain
The Gender Equality Index in Spain, calculated by the European Institute of Gender Equality, was 53.6 points in 2012, almost 5 points below that corresponding to the Basque Country.
Moreover, in 2012 the Basque Country obtained higher values than Spain in the partial indicators of five of the six dimensions taken into account in the calculation of the Gender Equality Index: the dimension in which the Basque Country most comfortably exceeded the result of Spain is Money, with a difference of 16.2 points. However, it also comes out in front in the dimensions of Power (+7.5), Time (+5.7), Health (+4.0) and Employment (+0.8). The only exception occurs in the dimension of Knowledge, in which Spain has a slight advantage (+0.9).
The gender gap is almost null in the indicators of Health and Income and very high in those of Economic Power
As well as the comparison with the European Union and its member countries, the internal situation in the Basque Country can be analysed using the gender gap concept, understood as the difference existing between men and women in the different areas described, the values of which range from 0 (total inequality) and 1 (total equality).

As a result, it can be seen that the gender gap is null or very slight in components related to health, such as Healthcare (1.00), Perception of own health (0.96), Life expectancy (0.96), Years in good health (0.97) and Dental Care (0.99). The gap is also very small in Sports, cultural and leisure activities (0.98) and Ongoing education (0.97).
On the other hand, the gender gap is very significant in Business Management (0.29), Public/Semi-public Bank Management (0.38), Segregation by activity sectors (0.52) and Segregation by field of study (0.62), where there remain substantial differences between genders.
Compared to 2010, there are both positive and negative trends, but standing out are the gender gap reduction in Domestic activities (from 0.69 to 0.79) and Childcare (from 0.85 to 0.94) and the negative trend of the indicator in Public/Semi-Public Bank Management (from 0.53 to 0.38).
METHODOLOGICAL NOTE
The Gender Equality Index (GEI) is a synthetic index that is calculated by aggregating 26 basic indicators. The GEI structure takes into account four levels:
1. The Gender Equality Index, maximum aggregation level
2. The Index of the six dimensions being studied: Employment, Money, Knowledge, Time, Power and Health.
3. The Index for the subdimensions that each of the previous dimensions are divided into.
4. The Index of the basic indicators, of which a measure of gender equality (M) is calculated for each.
The aggregation process that leads to the calculation of the Gender Equality Index occurs in the form of a scale that goes from level 4 to level 1 as follows:
The synthetic indices by subdimensions (S) are obtained by calculating the simple arithmetic mean for the measure of gender equality (M) for each basic indicator (X):
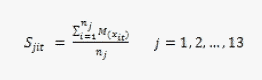
Where nj is the number of indicators included in each subdimension, and Sjit is the synthetic index for each subdimension, country and year.
The synthetic indices by dimensions (D) are obtained by calculating the geometric mean of the synthetic indices for the corresponding subdimensions (S):
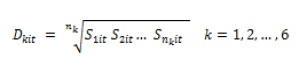
Where nk is the number of subdimensions included in each dimension and Dkit is the synthetic index for each dimension, country and moment in time.
The Gender Equality Index (GEI) is obtained by calculating the weighted geometric mean of the indices for each dimension (D):
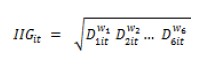
The weightings (w) utilised have been calculated by the European Institute for Gender Equality by applying the hierarchical clustering methodology.
List of basic indicators:
Full-time employment: Equivalent rate of full-time employment (percentage of the employed population aged 16 and above). Source: Eustat. Survey on Population in Relation to Activity and Economic Accounts
Working life duration: Working life duration (in years). Source: Eustat. Survey on Population in Relation to Activity and Demographic Indicators
Segregation by activity sectors: Employment in Education, Healthcare and Social Services (percentage of the employed population aged between 16 and 64). Source: Eustat. Survey on Population in Relation to Activity
Working flexibility for personal and family reasons: Proportion of the salaried and integrated population that feels it cannot balance working life with social and family obligations. Source: Department of Employment and Social Policies. Survey on Working Conditions
Work intensity: Proportion of the salaried and integrated population not satisfied with their rhythm of work. Source: Department of Employment and Social Policies. Survey on Working Conditions
Wages: Average net pay made by the salaried and integrated population (in euros for the last month paid). Source: Department of Employment and Social Policies. Survey on Working Conditions
Income: Average equivalent household income per capita of the population aged 16 and above (in euros). Source: Department of Employment and Social Policies. Survey on Poverty and Social Inequalities
Risk of poverty: Individuals not at risk of poverty, i.e. whose equivalent household income per capital is equal to or greater than 60% of the average income (percentage of the population aged 16 and above). Source: Department of Employment and Social Policies. Survey on Poverty and Social Inequalities
Distribution of income: Ratio between income quintiles 20 and 80 (percentage of the population aged 16 and above). Source: Department of Employment and Social Policies. Survey on Poverty and Social Inequalities
University studies: Individuals who have a tertiary/higher education qualification (percentage of the population aged 15 to 74). Source: Eustat. Survey on Population in Relation to Activity
Segregation by field of study: University students in the fields of Education, Health & Well-Being and Arts & Humanities (percentage of the population who have completed university studies). Source: Eustat. University Statistics
Ongoing education: Individuals in regulated/non-regulated education during the last four weeks (percentage of the population aged between 15 and 74). Source: Eustat. Survey on Population in Relation to Activity
Childcare: Employed individuals who have devoted an hour or more to childcare (percentage of the employed population aged 16 and above). Source: Eustat. Survey on Time Budgets
Domestic activities: Employed individuals who have devoted an hour or more to domestic activities (percentage of the employed population aged 16 and above). Source: Eustat. Survey on Time Budgets
Sports, cultural and leisure activities: Employed individuals who have devoted an hour or more to sports, cultural and leisure activities (percentage of the employed population aged 16 and above). Source: Eustat. Survey on Time Budgets
Voluntary and charity activities: Employed individuals who have devoted an hour or more to voluntary and charity activities (percentage of the employed population aged 16 and above). Source: Eustat. Survey on Time Budgets
Representation in Government: Gender distribution of Government members. Source: Prepared in-house with the relevant websites
Parliamentary Representation: Gender distribution of members of Parliament. Source: Prepared in-house with the relevant websites
Representation in Provincial Assemblies: Gender distribution of provincial assembly members. Source: Prepared in-house with the relevant websites
Business Management: Gender distribution of individuals who are part of a Board of Directors in large companies. Source: Prepared in-house with the relevant websites
Public/Semi-Public Bank Management : Gender distribution of individuals who are part of a Board of Directors in large companies. Source: Prepared in-house with the relevant websites
Perception of own health: Perception of own health as good or very good (percentage of the population aged 16 and above). Source: Department of Health. Health Survey of the Basque Country
Life expectancy : Life expectancy at birth (years). Source: Eustat. Demographic Indicators
Years in good health: Years in good health at birth. Source: Department of Health. Health Survey of the Basque Country
Healthcare: Individuals without health insurance not requiring healthcare (percentage of the population aged 16 or more). Source: Department of Health. Health Survey of the Basque Country
Dental care: Individuals without health insurance not requiring dental care (percentage of the population aged 16 or more). Source: INE (National Statistics Institute). Survey on Living Conditions
For further information:
Eustat - Euskal Estatistika Erakundea / Basque Statistics Institute
C/ Donostia-San Sebastián, 1 01010 Vitoria-Gasteiz
Press Service: servicioprensa@eustat.es Tel: 945 01 75 62