Press release dated 05/10/2010
HEALTH AT A GLANCE of the Basque Country - 2008
High life expectancies and low mortality rates in the Basque Country compared to Europe and with lower spending on health
We are at European levels in terms of the unhealthy habits of the population, amenities and public funding, although we go to the doctor more often
This is just some of the information that can be found in the "Health at a Glance of the Basque Country, 2008", a social report that is based on a synthesis statistical operation, conducted by Eustat in conjunction with the statistical entity of the Department of Health and Consumers.
This publication seeks to collect and synthesize health information: the key factors (environmental and behaviour), the state of health perceived and declared by the population, the health system (preventive practices, human and structural resources and their use), as well as providing comparison indicators that enable us to establish our position with other countries in our zone.
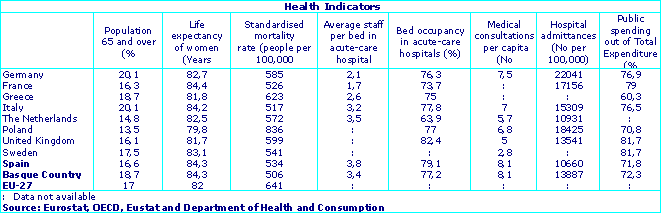
The demographic indicators, which reveal the size and break down of future and potential demand for health care, show that the percentage of population aged 65 and over in the Basque Country (18.6%) was among the highest in the EU-27 (17%) and proportion of children was among the lowest (12.6% compared to the 15.7% of the EU-27. The forecasts likewise point towards a moderate growth of the population.
In the same way as in other EU countries, the life expectancy for women in the Basque Country (84.3 years) was longer than for men (77 years); the values in both cases were higher than the average for the EU-27 (82 years for women and 76 years for men) and among the highest in Europe.
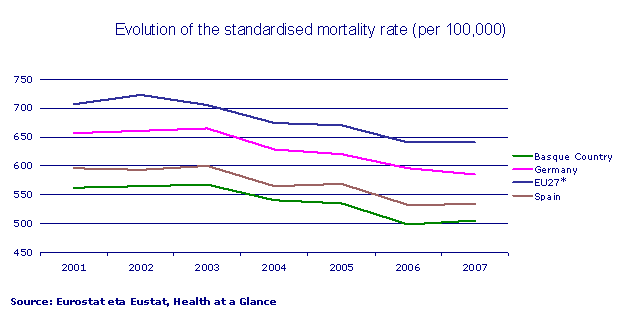
The mortality rate of the Basque Country (standardised to minimise the effect of the population structure by ages) came to 506 people per 100,000 inhabitants. This was under the EU-27 (641 per 100,000) and the differences by gender indicate that the mortality rate for men (687) was higher than for women (363).
Tumours were the main cause of death in the Basque Country (172 deaths per 100,000), followed very closely by diseases of the circulatory system (137), which had an incidence lower than the rest of EU-27 (246 deaths), where they were the first cause of death.
Among the unhealthy habits, men said that they consumed more alcohol than women. In the case of the Basque Country, the percentage of men that said that they had drunk alcohol in the last year was 91% (similar value to the United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Sweden) and 75% in the case of women (behind Sweden, the United Kingdom and Germany). This gender difference fell when it came to smoking, where the proportion of smokers was 29% among men compared to 21% among women.
Obesity generated numerous health problems. The proportion of obese population in the Basque Country was 13% in the case of men and 12% in the case of women and had also worsened in recent years, a situation shared with a significant number of EU-27 countries where it affected 15-20% of the population, except in German and the United Kingdom which posted higher figures.
If we compare staff and facilities, the Basque Country had a ratio of 3.4 hospital staff per hospital bed, which places it in the group to which the majority of OECD countries belong (between 2 and 4 people). As far as the use of the facilities was concerned, the occupancy percentage of the available beds in the acute-care hospitals of the Basque Country was 77%, a value that was close to the other countries in our zone.
As far as the population’s use of the available health resources was concerned, the Basque Country, with an annual average of 8.1 medical consultations per inhabitant, was among the OECD countries (7 consultations) that most use health care.
This was not the case when it came to hospital care, as the number of people admitted per 100,000 inhabitants places the Basque Country (with 13,887 people admitted) between the countries that obtain the lowest values in this indicator – together with the Netherlands, Spain, the United Kingdom – which was the outcome of the hospital care at home and the advances in medical science. In terms of the causes, diseases of the circulatory systems were quoted by both the Basque Country and the European Union-27 as the main reason for patients being admitted to hospital.
The Health Account of the Basque Country indicated that the annual average growth rate of the total expenditure of Health between 2000 and 2006 was 8.1%, reaching 6.9% in terms of GDP in 2006. In the international comparison of spending on Health per capital in terms of purchasing power parity, it was $2,446, slightly lower that the average for the OECD which stood at $2,760, even though the health indicators of the patient population, such as life expectancy and mortality, posted higher values than those for the average of the European Union-27.
In terms of funding, public expenditure in the Basque Country accounted for 72.3% of total spending, in line with the other countries in its zone where values ranged between 71 and 79%.
For further information:
Basque Statistics Office
C/ Donostia-San Sebastián, 1 01010 Vitoria-Gasteiz
Tlf:+34-945-01 75 00 Fax:+34-945-01 75 01 E-mail: eustat@eustat.eus
Contact: Marta de la Torre Fernández
Tlf:+34-945-01 75 48 Fax:+34-945-01 75 01
The full report is available at: Health at a Glance